DIABETES IN THE ELDERLY
Diabetes (diabetes mellitus) is a group of medical diseases, caused by a disturbance in insulin metabolism in the body, leading to high blood sugar levels. It is estimated that by 2030, the whole world will have more than 500 million people with diabetes and account for 80% of the medical burden in low-middle-income countries. Diabetes, especially type 2 diabetes, is the leading cause of blindness, hemodialysis and amputation in patients worldwide. At the same time, cardiovascular events such as myocardial infarction and stroke due to diabetes are also the leading causes of death.
In the human body, insulin is a hormone that helps to transport sugar in the blood to the cells of the body, or in other words, insulin is a hormone that helps the body regulate blood sugar and help cells The body’s cells can use the sugar added to the body’s metabolism. Diabetes (diabetes mellitus) can occur in almost any age group with many different causes. In the article below we will mention the most detailed information about diabetes in the elderly to help you better care for the health of the elderly with diabetes. Do not set too high demands on the elderly (in exercise, diet and drug use). Often in the elderly, it is possible to maintain a slightly higher blood sugar level than a young person. For the elderly in sick days, do not eat or eat poorly, they may not take medicine, in these cases, it is best to visit a specialist facility for appropriate advice.

https://au.shop.com/GETPAYWHILEUSHOP/Isotonix+reg+Isochrome+-1411051553-p+.xhtml?credituser=R4580320
Classify
What type of diabetes do you have?
There are three main types of diabetes, namely type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes (diabetes mellitus)
Type 1 diabetes, is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks pancreatic cells instead of external factors. This will cause a lack of insulin and an increase in blood sugar.
If you have type 1 diabetes, symptoms appear very early and at a relatively young age, usually in childhood or adolescence.
The exact cause of type 1 diabetes has not been determined. Doctors think that type 1 diabetes may be caused by a combination of genetics and environmental factors. However, you may be at higher risk for type 1 diabetes if:
Mother or sibling with type 1 diabetes.Exposure to certain disease-causing viruses.Presence of diabetes antibodies.Vitamin D deficiency, early use of cow’s milk or formula derived from cow’s milk, and eat cereals before 4 months of age. Although they do not directly cause type 1 diabetes, they do contribute to an increased risk. Countries such as Finland and Sweden, have relatively high rates of type 1 diabetes.

Diabetes (diabetes) type 2
Type 2 diabetes, also called non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM), is the most common type of diabetes, accounting for 90% to 95% of all patients diagnosed with diabetes. The disease usually appears in adulthood, but due to the increasing prevalence of obesity, more and more cases are now being detected in adolescents and young adults. You could have type 2 diabetes without you knowing it.
With type 2 diabetes, your cells become resistant to insulin, and the pancreas cannot make enough insulin to overcome this resistance. Instead of moving into cells for energy, sugar builds up in your blood.
The exact reason why is unknown, however, doctors believe that genetic and environmental factors are involved in the development of type 2 diabetes. Being overweight is a major risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes. develop type 2 diabetes, but not all people with type 2 diabetes are overweight.
Other types
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that occurs only in pregnant women. This disease can cause problems for both mother and baby if left untreated. However, gestational diabetes usually goes away after labor. Other types of diabetes are less common and can be caused by a genetic syndrome, surgery, medication, malnutrition, infection, or when have other diseases.
Diabetes insipidus, despite its similar name to the above types, is another condition caused by the kidneys losing their ability to store water. This condition is very rare and treatable.
1) What are the characteristics of diabetes in the elderly?
Because the characteristics of the elderly give rise to distinctive clinical features of diabetes in the elderly that differ from those in the general population, which are: (1) higher morbidity; (2) atypical symptoms; (3) diseases arise more and more severe; (4) when the diagnosis is prone to error; (5) high mortality rate. Therefore, doctors and patients need to pay more attention. Because the symptoms of diabetes in the elderly are not typical, it is easy to misdiagnose and misdiagnose, in general, in elderly diabetics, if symptoms are present, they are also very mild, such as not eating much, Drink a lot, pee a lot.
Quite a lot of elderly people have diabetes in the elderly, the disease only shows some chronic complications or some clinical manifestations, such as myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol. , and diabetic neuropathy, diabetic nephropathy and diabetic eye complication, diabetes was discovered through chemical examination.
In a small number of patients, it is not known until the occurrence of cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral vascular occlusion, etc. that they have diabetes, in some other patients, when the myocardial obstruction occurs, the heart beats arrhythmia, heart failure.vv… just randomly discovered diabetes.
In addition, many diabetes in the elderly are non-insulin dependent, with a healthy, rosy appearance, high spirits, good appetite, so it is easy to misunderstand or belittle.
There are quite a few people who have had the disease for a long time, the small arteries in the kidneys have been hardened, the kidney glucose threshold has been raised, only the urine test is incorrect, the diagnosis is not accurate, it is necessary to test more blood sugar to make a correct conclusion.
In summary, with diabetes in the elderly, the symptoms are often latent, atypical, if normally do not pay attention to the health check, so the disease is still not detected. The diagnosis is in the late stage, the treatment of diabetes in the elderly is too late, the effectiveness is not high, the consequences are unpredictable, so for the elderly, it is necessary to pay attention to proper vigilance.
2 . How dangerous is diabetes in the elderly?
In addition to the dangers that any person with diabetes must face, due to the unique characteristics of diabetes in the elderly, they also face their own dangers. It is therefore necessary to be fully aware of these particular dangers to ensure a healthy and long life for the elderly, and to reduce morbidity and mortality.
If diabetes in the elderly is accompanied by cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease, the disease is often serious, currently considered one of the factors that threaten the survival of the elderly, so if it is early Detecting diabetes in the elderly, for active treatment, is very important work.
In addition, diabetes complications that make the elderly disabled are also a constant threat, such as retinal complications, fundus hemorrhage, cataracts that cause blindness in the elderly. The peripheral nerve and cerebrovascular complications of diabetes often lead to gangrene, when the severity becomes severe, the leg is amputated, causing lifelong disability or death.
Patients do not drink much due to no or very little thirst, on the contrary they often complain because they feel weak, lose weight, or or have an infection… Another cause of diabetes in the elderly is that “the elderly” are often “reduced”. memory, or disease, depression, Alzheimer’s disease…
Therefore, the American Diabetes Association has recommended that all people over 45 years of age be screened for the disease every 3 years, while those with additional risks such as those in the family with diabetes should be screened for the disease. diabetes, coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, obesity, dyslipidemia… they need to be checked more often.
Because the threshold at which blood sugar must cross the kidney barrier also increases with age, it is only when blood sugar is very high that it can spill out in the urine, so diabetes cannot be diagnosed based on a glucose test in the water. urine.
3 . Some points to note when treating diabetes in the elderly
In addition to the general principles of diabetes treatment, when treating elderly diabetic patients, the following points must be paid attention to:
The goals of diabetes treatment in the elderly are to reduce the symptoms of high blood sugar, prevent the risk of infection and acute complications such as coma due to too high blood sugar.
– The blood sugar level to be achieved in the elderly may be higher than that of young people, specifically, the fasting blood sugar needs to be below 8.3mmol/l, and the postprandial blood sugar needs to be below 12.2mmol/l.
– Consequences of complications of hypoglycaemia due to overdose are extremely serious and often leave severe neurological sequelae. The manifestations of hypoglycemia in the elderly are very faint.
– Elderly patients can use most drugs to treat diabetes in the elderly, but it is imperative to have a thorough medical examination and check liver, kidney, and heart function… before deciding on treatment. The contraindications of each class of antidiabetic drugs must be strictly observed.
– At the beginning of treatment, blood sugar should be checked regularly both fasting, after meals and before going to bed… even if the patient has no symptoms of hypoglycemia.
– Controlling blood sugar with diabetes in the elderly can be very difficult and complicated because patients often have to take some other drugs such as thiazide diuretics to treat hypertension or heart failure, thyroid hormones. Thyroid treatment for hypothyroidism, corticosteroids for cancer treatment, chronic lung disease… are drugs capable of increasing blood sugar.
– When taking insulin, sometimes only 1 injections/day is enough, instead of 2-4 injections as in young patients.
– And finally, always remember to control diseases, other diabetes risk factors in the elderly such as high blood pressure, smoking, etc.
4 . Diabetes in the elderly
Because of the special physiological and pathological changes in the elderly (over 65 years of age), separate and more detailed studies of diabetes in the elderly are required. When the elderly have diabetes, it will be more difficult and complicated to treat.
Causes of increased prevalence of diabetes in the elderly are changes in glucose metabolism, insulin secretion disorders and insulin resistance increase with age, because the elderly are often required to take multiple drugs that affect the health of the elderly. blood sugar, due to a sedentary lifestyle and because they are often obese or overweight.With the principle that prevention is better than cure, detecting diabetes at an early stage is the best prevention measure. Early detection and timely intervention will reduce the extent or prevent complications of diabetes in the elderly.
These are usually vision loss, even blindness due to diabetes, lower limb amputation due to peripheral vascular disease, neurological disease and infection, ischemic heart disease, cerebrovascular accident, and renal failure. chronic… All of which reduce the quality of life of elderly people with diabetes.
5 . Caring for the elderly with diabetes
Not only does diabetes occur in the elderly, but they can also suffer from other age-related health problems. Therefore, taking care of elderly parents with diabetes requires a lot of knowledge and a combination of love.
Diabetes care in the elderly: To take good care of the elderly with diabetes, you first need to clearly distinguish two common diseases (type 1, type 2), treatment drugs, and complications. Dangers can occur and how to prevent…Dealing with hypoglycemia: In the treatment of diabetes in the elderly, it is very important to take medication according to the doctor’s instructions. However, antidiabetic drugs can also cause side effects when treating diabetes in the elderly, such as causing sudden low blood sugar. Hypoglycemia is a condition in which blood sugar drops below 10mg/dL. Symptoms of hypoglycemia include sweating, trembling, anxiety, irritability, etc. Elderly people often do not realize they are having low blood sugar or have difficulty describing the symptoms they are experiencing. encountered. Therefore, caregivers need to pay attention to the unusual changes of the patient, especially after taking medicine or exercising, in order to take timely intervention measures. So what to do when the patient has a sudden low blood sugar? If possible, check the patient’s blood sugar for less than 10mg/dL, if true, give them 1 teaspoon of quick-acting sugar or half a cup of fruit juice immediately. Check your blood sugar again 15 minutes later to make sure it’s up to 70mg/dL. The patient can be given a light meal with starchy foods such as bread, potatoes, rice, milk or fruit so that the blood sugar does not drop again.
What should you do when the patient suddenly has Hyperglycemia:
Hyperglycemia is also an effect of diabetes in the elderly. Hyperglycemia is a condition in which blood sugar levels rise to 200mg/dL. After eating, the patient often has a rise in blood sugar, this is normal.
However, if blood sugar rises too high, the patient may experience symptoms such as thirst, increased urination, fatigue, hunger and irritability. If left untreated, hyperglycemia can lead to kissing. passionate about.
The main cause of this condition is due to too much carbohydrate in the meal, skipping/forgetting to take medicine or taking the wrong dose. Infections or stress can also cause hyperglycemia.You should take the patient to see a doctor to adjust the dose accordingly.
Diabetic hyperosmolar coma (HHNK):
This condition can occur in elderly people with type 2 diabetes if they become infected and dehydrated. Symptoms of HHNK are confusion and loss of consciousness. Blood sugar can rise above 1,000mg/dL and lead to death. The patient needs to be taken to the emergency room immediately.
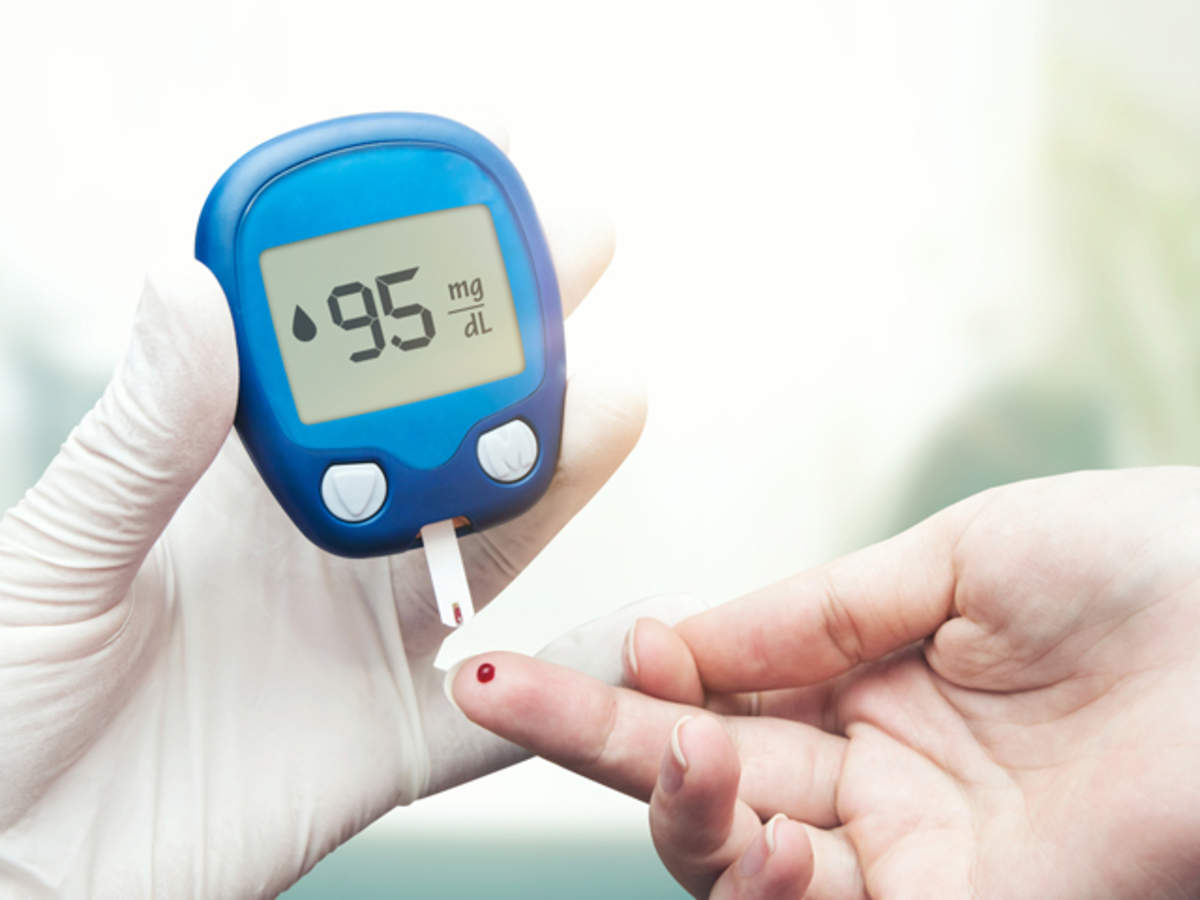
Foot care for the elderly with diabetes:
Foot care is important for diabetes in the elderly, especially the elderly because it is often difficult for them to do it on their own.
People with long-term diabetes often lose feeling in the feet, so if not taken care of, ulcers will appear in this location. Caregivers need to regularly check the feet, between the toes to detect cuts, sores or wounds for timely treatment. This should be done in conjunction with daily foot hygiene.
Infection in the feet is an extremely dangerous complication not only in young people but also of diabetes in the elderly that can quickly spread to the bones, leading to osteomyelitis. This condition should be treated promptly with antibiotics, in case of failure of treatment, the patient may have to amputate the leg.
Do exercise:
Caring for diabetes in the elderly with nutrition and exercise are the three basic elements in diabetes control. For elderly patients, exercise, even simple movements, also contributes to improving health. Caregivers should encourage their parents/relatives to exercise to
prevent dangerous complications of diabetes and prolong life.
6 . How to prevent diabetes in the elderly:
In general, maintaining a normal state of mind, ensuring quality of life, here are some specific measures:
Physical health training; Control your eating and drinking properly:
The elderly, if actively participating in physical training to increase physical strength, ensure their limbs are active, prevent excess fat leading to obesity and diabetes in the elderly. However, exercise cannot be too strong, too much, should only apply gentle forms such as walking, practicing tai chi, cycling in place.
Besides, it is necessary to arrange a certain exercise time, with an appropriate amount of exercise. This will have the effect of increasing blood circulation, fighting obesity, on the other hand, controlling the amount of calories absorbed during the day.
With diabetes in the elderly should eat frugally, choose foods that are easy to digest, absorb, high in fiber such as green vegetables and less sweet fruits. Limit foods rich in protein such as egg yolks, animal organs.
Blood sugar lowering supplements:
If only relying on eating control and participating in exercise, diabetes in the elderly cannot control diabetes effectively, but must be combined with the use of blood sugar-lowering drugs or supplements
When taking the drug should start from a small dose onward, then gradually increase as needed. The use of drugs should always be cautious, to prevent hypotension in the elderly, the consequences are very serious.
Natural ingredient supplements that lower blood sugar using a highly effective natural form can include Isotonix® Isochrome
in combination with Isotonix® OPC-3
Prevention and treatment of emerging diseases:
The biggest threat to diabetes in the elderly is the co-morbidities associated with diabetes. Therefore, treating these co-occurring diseases plays a very important role, in order to maintain normal health, stable living capacity for diabetes in the elderly and prolong their life expectancy. .In addition, the risk of hypertension in the elderly is very high, so doctors need to have an arm blood pressure monitor to regularly check at home. Actively control the metabolism of sugar, fat, and protein at normal levels, which is a way to recover from complications such as pain and numbness.
With diabetes in the elderly, it is also necessary to involve families, relatives, and those who directly care for the patient in order to achieve the goal of prevention and treatment for the patient. Wish you have a healthy body.












